Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a key economic indicator that measures the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders during a specific period, typically a quarter or a year. GDP serves as a critical metric for assessing the economic health and size of a country’s economy. It’s often used to compare different countries’ financial performance or track a single country’s economic growth over time.
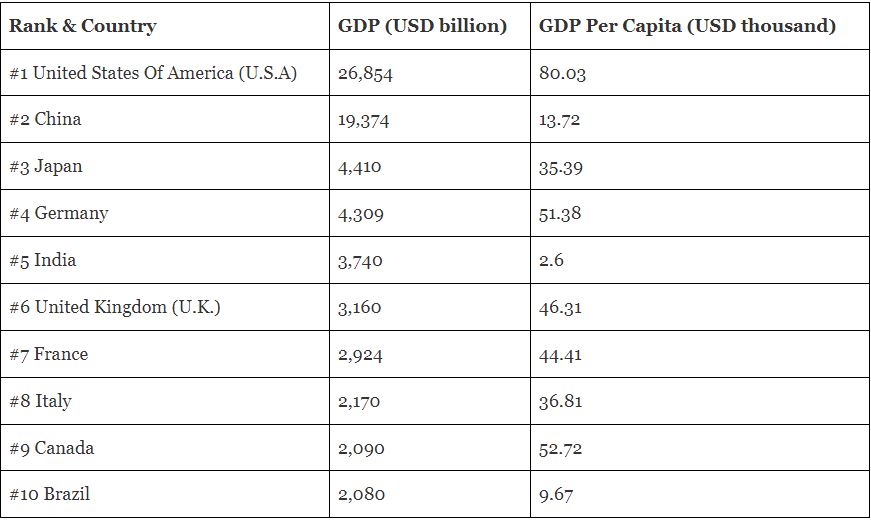
I noticed that many of our readers from India are looking for the GDP rank status of India in 2023, and the good news is that India is now in the 5th position in the world’s economic growth. So here I am sharing the exact info via the Upcoming Generation blog.
There are three primary ways to calculate GDP:
Production Approach (Output Method): This approach calculates GDP by summing up the value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders. It includes the importance of consumer goods, investments, government spending, and net exports (exports minus imports).
Expenditure Approach:
This approach calculates GDP by adding up all the spending within a country. It’s represented by the equation: GDP = C + I + G + (X – M), where:
- C represents household consumption expenditure.
- I represent a gross private domestic investment.
- G represents government spending.
- X represents exports of goods and services.
- M represents imports of goods and services.
Income Approach:
This approach calculates GDP by summing all the incomes earned within a country, including wages, rents, profits, and taxes (minus subsidies). The equation represents it: GDP = Compensation of Employees + Gross Operating Surplus + Gross Mixed Income + Taxes on Production and Imports – Subsidies.
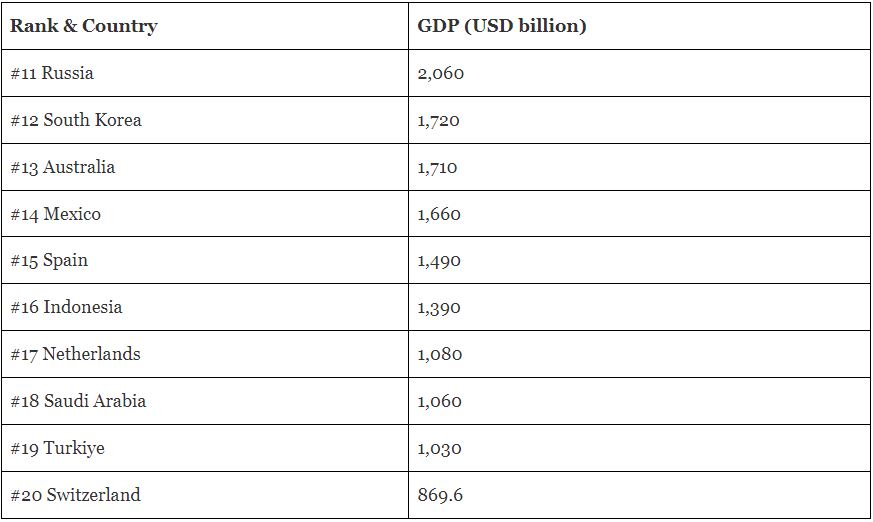
The image snapshot was taken from ForbesIndia website, Here are the next counties rank chart below:
GDP is typically expressed in nominal terms (current prices) and actual terms (constant prices adjusted for inflation). Real GDP allows for a more accurate comparison of economic output over time, as it removes the effects of inflation.
GDP is a vital tool for policymakers, economists, and investors because it provides insights into the overall economic performance of a nation. It can help assess trends, economic growth or recession, and the standard of living within a country. However, it’s important to note that GDP alone does not capture the full complexity of economic well-being, as it doesn’t consider factors like income distribution, environmental sustainability, or quality of life. To address these limitations, other indicators and measures are often used in conjunction with GDP.